Research
Please see Google Scholar for a full list of publications.
Polygenic Risk Prediction

While polygenic risk scores (PRS) become increasingly robust with increasingly larger GWAS, there are considerable debates about its clinical utility. We develop enhanced algorithms and software tools for improving the predictive utility and transferability of polygenic risk prediction models across diverse populations and complex human traits.
- Jin, J., Zhan, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, R., O’Connell, J., Jiang, Y., Aslibekyan, S., Auton, A., Babalola, E., Bell, R.K., et al. MUSSEL: Enhanced Bayesian polygenic risk prediction leveraging information across multiple ancestry groups. Cell Genomics, 4(4), 100539, 2024. [PDF] [Software]
- Dun, Y., Chatterjee, N., Jin, J.\(^*\), Nishimura, A\(^*\). A Robust Bayesian Method for Building Polygenic Risk Scores using Projected Summary Statistics and Bridge Prior, arXiv, 2024. [PDF]
- Zhang, H., Zhan, J., Jin, J., Zhang, J., Ahearn, T., Yu, Z., O’ Connell, J., Jiang, Y., Koelsch, B., 23andMe research team, Lin, X., Garcia-Closas, M., Chatterjee, N. A New Method for Multiancestry Polygenic prediction Improves Performance across Diverse Populations. Nature Genetics, 55(10), 1757-1768, 2023. [PDF]
[Software] [Code] - Zhang, J., Zhan, J., Jin, J., Ma, C., Zhao, R., Connell, J.O., Jiang, Y., 23andMe Research Team, Koelsch, B.L., Zhang, H., Chatterjee, N. An Ensemble Penalized Regression Method for Multi-ancestry Polygenic Risk Prediction. Nature Communications, 15(1), 3238, 2024. [PDF]
[Software] [Code] - Yu, Z., Jin, J., Tin, A., Kottgen, A., Yu B., Chen J., Ballantyne, C.M., Hoogeveen, R.C., Arking, D.E., Chatterjee, N., Coresh, J., Grams, M.E., Coresh J. Polygenic Risk Scores for Kidney Function to the Circulating Proteome, and Incident Kidney Diseases: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Community Study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 2021. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020111599.
[PDF]
(This work was selected by the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) as the “Best of ASN Journals” in 2021.) - Rabinowitz, J.A., Jin, J., Kahn, G., Kuo, S.I., Campos, A., Renteria, M., Benke, K., Wilcox, H., Ialongo, N.S., Maher, B.S. and others. Genetic Propensity for Risky Behavior and Depression and Risk of Lifetime Suicide Attempt among Urban African Americans in Adolescence and Young Adulthood. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 2021. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32866. [PDF]
- Rabinowitz, J., Jin, J., Kuo, S., Thrul, J., Reboussin, B., Domingue, B., Ialongo, N., Maher, B.,Uhl, G. Positive Associations between Cannabis and Alcohol Use Polygenic Risk Scores and Phenotypic Opioid Misuse among African-Americans. PLOS One, 17(4), p.e0266384, 2022. [PDF]
Integrative risk prediction models for human diseases

Large-scale epidemiologic studies, including modern genome-wide association studies (GWAS), are now rapidly leading to the identification of novel risk factors for human diseases. To summarize these findings into more effective strategies for reducing disease burden, a critical step is to advance risk prediction tools that predict future risk of diseases for healthy individuals and precision medicine to guide treatment strategies for targeted groups of patients.
- Jin, J.\(^*\), Agarwala, N.\(^*\), Kundu, P.\(^*\), Harvey, B., Zhang, Y., Wallace, E., , Chatterjee, N. Individual and Community-level Risk for COVID-19 Mortality in the United States. Nature Medicine, 27(2), 264-269, 2021. [PDF] [Code] [Online Tools]
- Ballreich, J., Jin, J., Kundu, P., Chatterjee, N. Provider and Patient Characteristics of Medicare Beneficiaries Who Are High-Risk for COVID-19 Mortality, Journal of General Internal Medicine, 36(7), 2189–2190, 2021. [PDF]
High-dimensional tests for disease-associated gene pathways
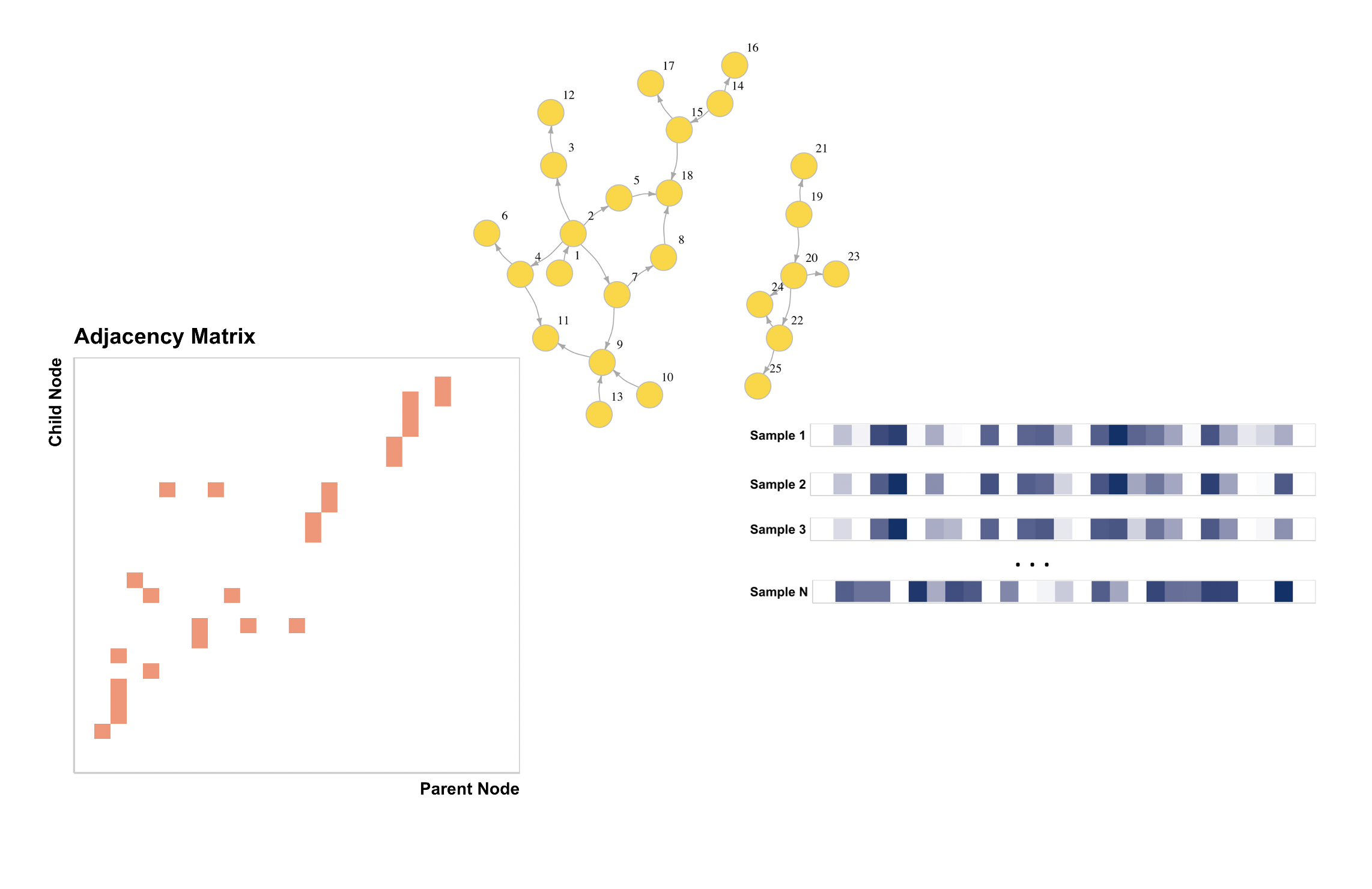
A major task in genetic studies is to identify genes related to human traits/diseases. Compared to marginal analyses of individual genes, detecting gene pathway, i.e., gene sets with known interactions that collectively contribute to some biological functions, can provide more biologically meaningful results. Due to the typically limited sample sizes, such analyses are usually high-dimensional, where the existing tests tend to have compromised power since they do not or only inefficiently incorporate the external pathway information on gene interactions.
I collaborated with Dr. Yue Wang from Arizona State Univeristy and proposed a graph-informed test which efficiently leverages the auxiliary pathway information via structural equation modeling to improve the estimation of the precision matrix.
- Jin, J., Yue, W. T2-DAG: A Powerful Test for Differentially Expressed Gene Pathways via Graph-informed Structural Equation Modeling. Bioinformatics, btab770, 2021. [PDF] [Code]
Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis for latent exposures

Recent MR research has focused on improving robustness to the presence of pleiotropic associations, by which genetic instruments can affect the outcome independent of the exposure and thus leading to the violation of key assumptions. I investigated a novel setting of pleiotropic association where genetic variants might be associated with multiple observed traits through an underlying latent exposure which may have a causal effect on the outcome.
- Jin, J., Qi, G., Yu, Z., Chatterjee, N. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Using Multiple Biomarkers of an Underlying Common Exposure. Under Revision. [PDF] [Code] [Slide]
MpMRI-based classification of Prostate cancer (PCa)
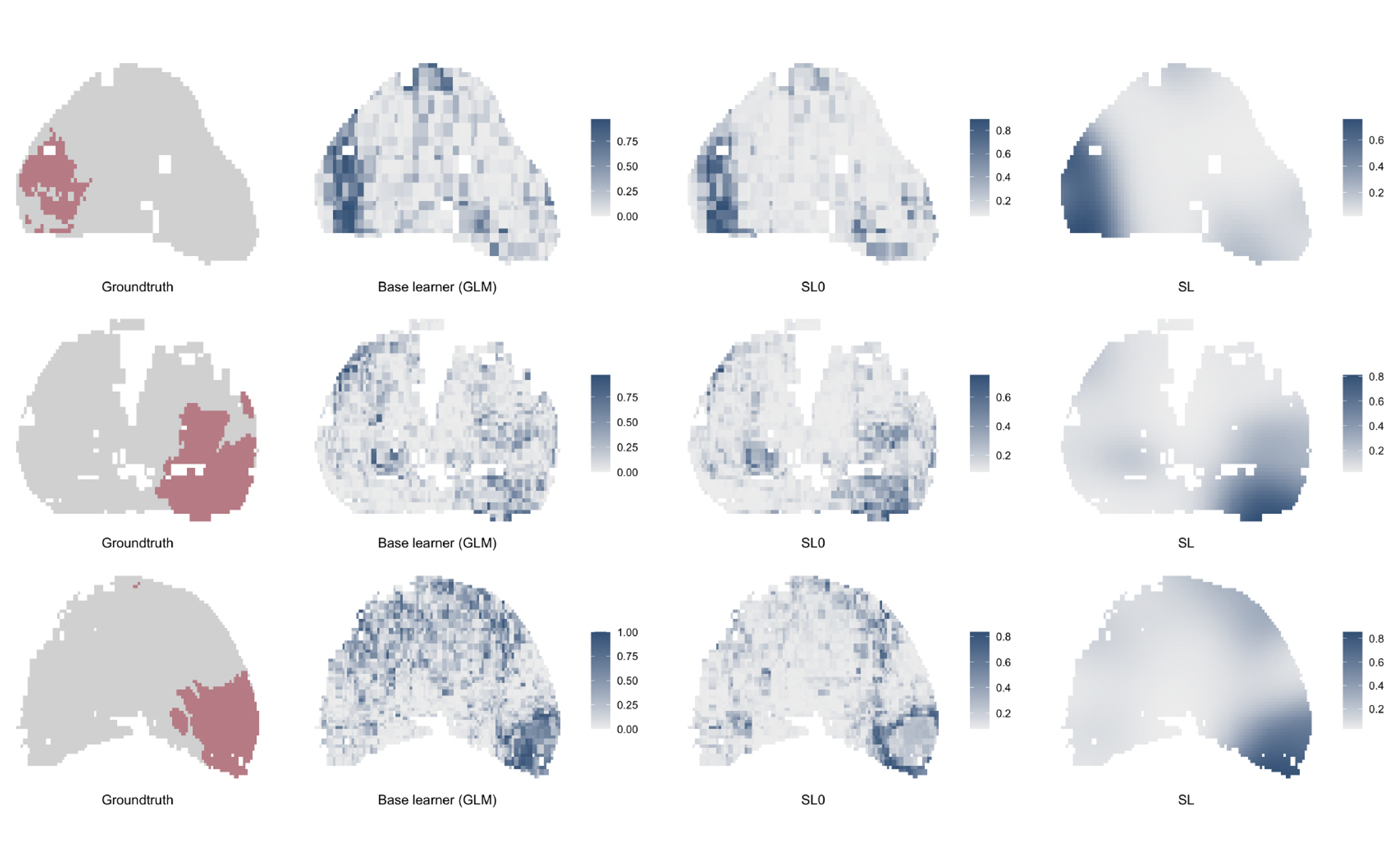
My research during the Ph.D. program focused on voxel-wise PCa detection using mpMRI, a critical tool in PCa diagnosis and management. MpMRI examinations are currently interpreted manually which is limited due to inter-reader variability. Automatic, quantitative predictive methods are thus proposed to address these limitations. We identified critical issues of the existing methods and developed scalable, high-field MRI-based Bayesian and machine learning-based classifers that can be used as non-invasive tools to assist clinicians with PCa diagnosis and treatment.
- Jin, J., Zhang, L., Leng, E., Metzger, G.J., Koopmeiners, J.S. Bayesian Spatial Models for Voxel-wise Prostate Cancer Classification Using Multi-parametric MRI Data. Statistics in Medicine, 1-17, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.9245. [PDF] [Code]
- Jin, J., Zhang, L., Leng, E., Metzger, G.J., Koopmeiners, J.S. A Multi-resolution Super Learner Algorithm for Voxel-wise Classification of Prostate Cancer Using Multi-parametric MRI. To appear in Journal of Applied Statistics, 2021. [PDF] [Code]
- Leng, E., Spilseth, Leng, E., Henriksen, J.C., Rizzardi, A.E., Jin, J., Nam, J.W., Brassuer, B.M., Johnson, A.D., Reder, N.P., Koopmeiners, J.S., Schmechel, S.C., Metzger, G.J. Signature Maps for Automatic Identification of Prostate Cancer from Colorimetric Analysis of H&E-and IHC-stained Histopathological Specimens. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1-12, 2019. [PDF]
- Jin, J., Zhang, L., Leng, E., Metzger, G.J., Koopmeiners, J.S. Detection of Prostate Cancer with Multiparametric MRI Utilizing the Anatomic Structure of the Prostate. Statistics in medicine, 37(22), 3214-3229, 2018. [PDF] [Code]
- Leng, E., Spilseth, B., Zhang, L., Jin, J., Koopmeiners, J.S., Metzger, G.J. Development of A Measure for Evaluating Lesion-wise Performance of CAD Algorithms in the Context of MpMRI Detection of Prostate Cancer. Medical Physics, 45(5), 2076-2088, 2018. [PDF]
Early-phase oncology trial design

As oncology research are focusing more on the genomic aberrations potentially shared by multiple cancer types, basket trials have been proposed to assess the efficacy of a new treatment simultaneously on multiple cancer types. But even with shared genetic aberration, different cancers may respond to treatments differently. I collaborated with a research team at Sanofi to develop novel Bayesian methods for detecting treatment efficacy and proof of concept (PoC) in early-phase basket trials by flexible borrowing according to sample similarity measured by the distance between posterior distributions of the treatment effects.
- Jin, J., Riviere, M.K., Luo, X., Dong, Y. Bayesian Methods for the Analysis of Early-phase Oncology Basket Trials with Information Borrowing across Cancer Types. Statistics in Medicine. 39(25), 3459-3475, 2020. [PDF] [Code]
- Jin, J., Liu, Q., Zheng, W., Shun, Z., Lin, T.T., Gao, L., Dong, Y. A Bayesian Method for the Detection of Proof of Concept in Early Phase Oncology Studies with a Basket Design. Statistics in Biosciences. 12, 167-179, 2020. [PDF] [Code]